Preventing Drips and Drops: Guide to Crankshaft Oil Seal Functionality

Your car’s engine is a symphony of moving parts, and at the heart of it all lies the crankshaft, spinning tirelessly to translate power. But what keeps this vital component lubricated and protected? Enter the crankshaft oil seal, an often overlooked yet crucial element.
Imagine a tiny gatekeeper, diligently holding back engine oil while simultaneously shielding the crankshaft from external contaminants. That’s the essence of a crankshaft oil seal.
These unsung heroes come in various forms, from the front crank seal guarding the engine’s timing system to the rear main seal acting as the final barrier against leaks. Crafted from robust materials like rubber or fluorocarbon, they withstand immense pressure and heat, ensuring smooth operation and optimal engine performance.
The efficient functioning of an engine relies on critical components, with the crankshaft oil seal playing a pivotal role.
This small yet essential part prevents oil leakage and maintains optimal lubrication, ensuring smooth engine operation.
Understanding the significance of the crankshaft oil seal is crucial for maintaining the longevity and performance of any vehicle.
What Is A Rear Crankshaft Oil Seal?
A rear crankshaft oil seal is a component in an internal combustion engine located at the rear of the crankshaft. Its primary function is to prevent oil leaks and ensure that oil does not escape from the engine through the rear of the crankshaft.
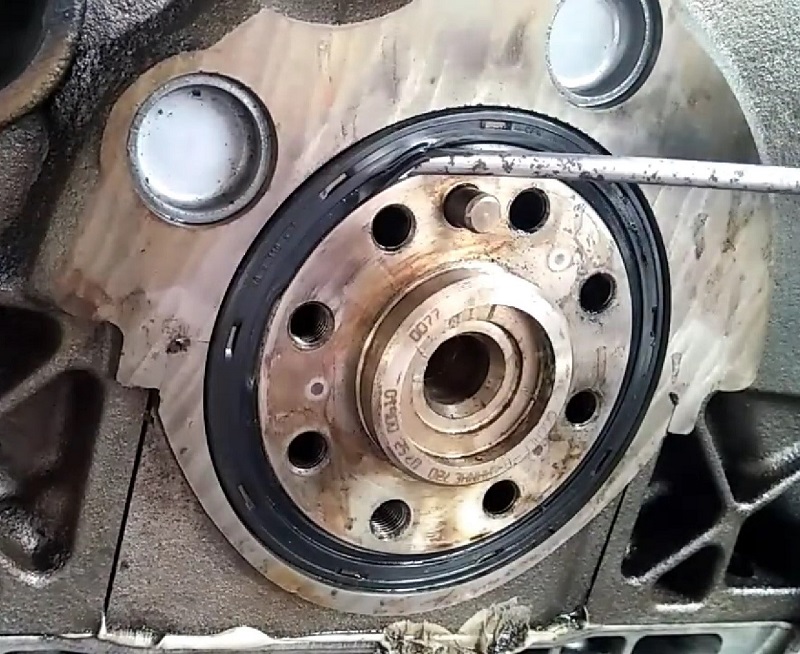

Function Of Crankshaft Seal
- Prevents oil leaks: Crankshaft seals form a barrier to contain engine oil within the crankcase.
- Protects internal components: Helps prevent contaminants from entering the engine, maintaining a clean and efficient environment.
- Ensures proper lubrication: Seals help retain lubricating oil around the crankshaft, promoting smooth operation.
How Serious Is A Crankshaft Seal Leak?
While a small leak might not cause immediate problems, it’s crucial not to ignore it. Here’s why:
- Oil Loss: Leaks can deplete engine oil, leading to lubrication issues, increased friction, and premature wear on internal components.
- Contamination: Leaking oil can contaminate belts, clutch components, or transmission fluid, impacting their performance and lifespan.
- Fire Risk: Leaking oil near hot engine parts poses a fire hazard.
- Environmental Impact: Leaking oil harms the environment and can lead to fines.
Rear Main Seal Replacement Cost
Here’s a general estimate of the total cost to replace a rear main seal:
- Low-end: $400-$800 (for simpler vehicles or independent shops)
- Mid-range: $800-$1200 (typical range for most vehicles)
- High-end: $1200-$2000+ (for complex vehicles, dealerships, or additional repairs needed)
Crankshaft Seal Replacement Cost
Here’s a general estimate of the total cost to replace a crankshaft seal:
- Low-end: $300-$700 (for simpler vehicles or independent shops)
- Mid-range: $700-$1000 (typical range for most vehicles)
- High-end: $1000-$1500+ (for complex vehicles, dealerships, or additional repairs needed)
Read More About Unlock Efficiency With The TOP 7 Best Oil Seal Removal Tool In 2024
Dt466 Front Crank Seal Replacement
Here’s an overview of the process and some key points to remember:
- Accessing the Seal
This usually involves removing the fan, belts, radiator, and harmonic balancer.
- Seal Removal
Use the appropriate puller to carefully remove the old seal without damaging the crankshaft surface.
- Cleaning and Inspection
Thoroughly clean the crankshaft surface where the new seal will sit, removing any dirt, debris, or old gasket material.
- Seal Installation
Carefully press the new seal onto the crankshaft using a suitable tool or your fingers, ensuring it sits flush and level.
- Reassembly
Reinstall the harmonic balancer, belts, fan, radiator, and other components in the reverse order of removal, torquing everything to the specified values.
- Refill Fluids
Refill the engine oil and coolant with the recommended type and quantit.
What Causes A Crankshaft Seal To Leak
- Age and wear: Over time, seals degrade.
- Poor installation: Incorrect installation can damage the seal.
- Excessive crankshaft movement: Wear or damage can cause excessive movement.
- High engine temperatures: Excessive heat can accelerate seal deterioration.
- Contaminants: Dirt, debris, or other particles can damage the seal.
- Harsh operating conditions: Extreme conditions can contribute to seal failure.
- Use of improper fluids: Incompatible fluids can damage the seal material.
- Manufacturer defects: Poor quality or manufacturing defects in the seal.
Rear Crankshaft Oil Seal Leak Symptoms
- Oil puddles or drips beneath the vehicle
- Burning oil smell from the engine
- Low oil levels despite regular top-ups
- Visible oil leakage around the rear of the engine
- Engine misfires or runs poorly
- Reduced oil pressure warning light
- Increased exhaust smoke, especially blue or gray
- Unusual engine noises, such as knocking or tapping
- Difficulty in maintaining proper engine lubrication

Rear Crankshaft Oil Seal Replacement
- Ensure the vehicle is safely lifted and supported.
- Remove the transmission or access panel.
- Locate the rear crankshaft seal.
- Use a seal removal tool to carefully extract the old seal.
- Clean the surrounding area thoroughly.
- Lubricate the new seal and install it evenly.
- Use a seal installation tool or a block of wood to seat the seal.
- Reassemble the transmission or access panel.
- Start the engine and check for leaks.
Rear Crankshaft Oil Seal Replacement Cost
- Labor Costs: Replacing the rear main seal often involves removing the transmission or engine, resulting in several hours of labor. Expect 3-8 hours of work, translating to costs ranging from $350 to $750+.
- Parts Cost: The seal itself is relatively inexpensive, typically costing between $30 and $80. However, additional parts like gaskets, fluids, and cleaning supplies can add to the total cost.
Rear Crankshaft Oil Seal Location
The rear crankshaft oil seal is located at the point where the engine’s crankshaft attach to the tranny, preventing oil leaks.
How To Fix Rear Crankshaft Oil Seal
Here is a general guide on how to fix a rear crankshaft oil seal:
- Raise the Vehicle: If working from underneath, lift the vehicle using a jack and secure it with jack stands.
- Remove Transmission or Engine: If it’s behind the engine, you may need to remove the engine.
- Locate the Rear Crankshaft Oil Seal: It is typically located at the rear of the engine block.
- Remove the Old Seal: Use a screwdriver or pry bar to carefully remove the old seal. Be cautious not to damage the surrounding components.
- Install the New Seal: Apply a small amount of oil to the new seal to aid in installation. Carefully install the new seal into the designated groove, making sure it is seated evenly.
- Reassemble: If you removed the transmission or engine, reassemble the components in the reverse order of removal.
- Refill Fluids: If you removed the transmission or drained any fluids, refill them according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Test: Start the engine and check for any leaks.
Chevy Rear Crankshaft Oil Seal
The Chevy rear crankshaft oil seal is a vital component that prevents oil leaks from the engine. It is situated at the rear of the crankshaft, providing a barrier against oil seepage.
Crankshaft Oil Seal Problems
- Oil leaks around the crankshaft can indicate a faulty crankshaft oil seal.
- Common issues include wear and tear over time.
- Improper installation during engine assembly can lead to seal failure.
- Excessive heat or high engine temperatures may accelerate seal deterioration.
Repeated Rear Main Seal Failure
Causes of Repeated Failure:
- Improper installation: This is the most common cause. If the initial repair wasn’t done correctly, the seal might not be seated properly, leading to leaks again.
- Incorrect seal selection: Using the wrong seal type or size for your specific engine can cause improper fit and leaks.
- Underlying engine issues: Worn crankshaft surfaces, excessive crankshaft end play, or warped rear bearing housing can create conditions that damage or stress the seal, leading to repeated failure.
- Low-quality seal: Using cheap or non-OEM seals might not be as durable or resistant to wear, leading to earlier failure.
- Installation damage: During the repair process, the crankshaft surface or seal itself could be inadvertently damaged, compromising its integrity and leading to leaks.
Blue Devil Main Seal Stop Leak
This product claims to stop rear main seal leaks by conditioning and revitalizing the existing seal, supposedly allowing it to swell and fill minor gaps.
5.7 Vortec Front Main Seal
The 5.7 Vortec front main seal is a crucial component in the engine, preventing oil leaks and ensuring proper lubrication. Regular inspection and replacement are recommended for optimal engine performance and longevity.
Read Also Boon Or Bust : Ford Ranger Catch Can Problems To Solutions
Ford 4.2 Front Crank Seal
The Ford 4.2 front crank seal is a crucial component in the engine, preventing oil leaks. Regular inspection and replacement ensure proper functioning and longevity of the seal, maintaining engine performance.
Jeep 4.0 Front Main Seal Replacement
- Remove the fan and shroud for easier access.
- Loosen and remove the serpentine belt.
- Disconnect the harmonic balancer.
- Use a puller to remove the balancer.
- Remove the front cover bolts.
- Carefully pry off the front cover.
- Access and replace the front main seal.
- Clean the sealing surfaces.
- Apply sealant to the cover.
- Reinstall the front cover and harmonic balancer.
- Tighten all bolts to specifications.
- Reinstall the serpentine belt, fan, and shroud.
How To Replace Crankshaft Seal Toyota Camry
- Lift the front of the Toyota Camry using a jack and secure it on jack stands.
- Remove the drive belts and the crankshaft pulley.
- Access the old crankshaft seal by removing the timing belt or timing chain cover.
- Use a seal puller or a screwdriver to carefully pry out the old crankshaft seal.
- Clean the area around the seal housing.
- Apply a small amount of oil to the new crankshaft seal and press it into place.
- Reassemble the components, including the timing belt or timing chain cover, crankshaft pulley, and drive belts.
- Lower the vehicle and start the engine to check for leaks.
How To Replace Crank Seals On A 2 Stroke
- Gather necessary tools: screwdrivers, socket set, seal puller, and replacement seals.
- Disconnect spark plug wire and drain gearbox oil.
- Remove the side cover and loosen the flywheel nut.
- Use a flywheel puller to remove the flywheel.
- Locate and remove the old crank seals using a seal puller.
- Clean the seal areas thoroughly.
- Install new crank seals with a seal driver tool.
- Reassemble the flywheel, side cover, and tighten the nut.
- Refill gearbox with the appropriate oil.
- Reconnect the spark plug wire and test the engine.
Crankshaft Seal Vs Rear Main Seal
Here’s a simple table outlining the key differences between a crankshaft seal and a rear main seal:
| Feature | Crankshaft Seal | Rear Main Seal |
| Location | Positioned on the crankshaft, usually at the front or rear. | Specifically located at the rear of the engine, sealing the interface between the engine block and the crankshaft. |
| Purpose | Prevents oil leakage from the crankshaft to the outside of the engine. | Seals the gap between the rear of the crankshaft and the engine block to prevent oil leaks. |
| Components | Can be made of rubber, silicone, or other materials. | Typically made of rubber or a combination of rubber and metal. |
| Replacement | May need replacement if it starts leaking or shows signs of wear. | Replacement is required if there is oil leakage or if it is damaged, as it is critical for preventing oil from escaping the engine. |
| Common Issues | Oil leaks, which can lead to lubrication problems and engine damage. | Oil leaks can lead to a drop in oil pressure, potential damage to the clutch (in manual transmissions), and environmental pollution. |
| Maintenance | Regular inspection is advisable during routine engine maintenance. | Regular inspection is essential during engine maintenance, especially when experiencing oil-related issues. |
| Position in Engine | Front crankshaft seal is positioned near the harmonic balancer, and rear crankshaft seal is positioned at the back near the flywheel or flexplate. | Positioned at the rear of the engine, usually between the engine block and the transmission b |

What Happens If Oil Seal Is Broken?
Potential Consequences:
- Lubrication Issues: Reduced oil levels lead to insufficient lubrication of internal engine components, increasing friction and wear. This can lead to premature component failure and engine damage.
- Overheating: Without proper lubrication, engine components generate excessive heat, further exacerbating wear and potentially leading to overheating and engine seizure.
- Contamination: Leaking oil can contaminate belts, clutch components, or transmission fluid, impacting their performance and lifespan.
- Fire Risk: Leaking oil near hot engine parts presents a fire hazard.
- Environmental Impact: Leaking oil harms the environment and can lead to fines.
Read Also 7 Common Flashlube Catch Can Problems & Solutions
FAQs
What Does A Crankshaft Oil Seal Do?
A crankshaft oil seal prevents oil leakage from the engine by sealing the gap between the crankshaft and the engine block. It helps maintain proper lubrication and prevents contaminants from entering.
How Long Do Crankshaft Oil Seals Last?
Crankshaft oil seals typically last around 100,000 miles under normal driving conditions.
How do you stop a crankshaft leak?
To stop a crankshaft leak, identify the source of the leak, assess the severity, and then apply an appropriate sealant or gasket. Professional assistance may be needed for extensive damage.
Can a crankshaft fail?
Yes, a crankshaft can fail due to various reasons such as fatigue, excessive stress, manufacturing defects, or lack of lubrication, leading to engine damage and potential catastrophic failure.
Can you drive with a leaking crankshaft seal?
Driving with a leaking crankshaft seal is not recommended. It can lead to oil loss, engine damage, and potential safety hazards. Immediate repairs are advisable to prevent further issues.
How many seals does a crankshaft have?
A crankshaft typically has two seals – one at the front and another at the rear.
When should I replace my oil seals?
Replace oil seals when they show signs of leakage, wear, or damage. Regularly check for oil puddles under your vehicle, as this may indicate a need for oil seal replacement.
center>
Conclusion
The integral component ensuring engine functionality lies in the crankshaft oil seal. This vital seal prevents oil leakage, maintaining optimal lubrication within the engine. Its significance in safeguarding against potential damage underscores the critical role it plays in preserving engine performance and longevity.