How Does A Supercharger Work- Types, Principle & More
Unlock the secrets of superchargers! Learn how a supercharger works, boosting engine power and performance. Dive into the mechanics of supercharger technology.
A supercharger is a performance-enhancing device for internal combustion engines. It’s essentially an air compressor that forces more air into the engine, allowing for more fuel to be burned and consequently, more power to be produced. A supercharger is mechanically driven by the engine, using a belt connected to the crankshaft.
As the supercharger compresses the incoming air, it increases the oxygen supply, allowing for more fuel combustion and significantly boosting horsepower and torque in internal combustion engines.
Lets find out more about supercharger.
What Is A Supercharger?
A supercharger enhances internal combustion by mechanically compressing intake gas, increasing air intake for greater power within a given displacement. Unlike a turbocharger, it’s driven by a belt from the crankshaft, not exhaust gases’ kinetic energy.
Families Of Superchargers
Superchargers are categorized into dynamic superchargers and positive displacement.
Positive displacement provides consistent boost pressure, while dynamic ones increase pressure exponentially with engine speed.
Dynamic superchargers, though rare, exist. Roots blowers are 40-50% efficient at high boost, while Lysholm-style blowers can rival dynamic superchargers in specific conditions.

Read More about Oil Catch Can: Shield Your Engine, Boost Its Power
Different Types Of Supercharger
There are several types of superchargers, each with its own characteristics. The main types include:
1. Roots Supercharger
Also known as a positive displacement blower, the Roots supercharger is one of the oldest and simplest designs. It uses lobes or rotors to move air in a fixed volume, delivering a consistent amount of air with each revolution.
2. Centrifugal Supercharger
Operates using a spinning impeller similar to a turbocharger, compressing air before it enters the engine. Provides a more gradual increase in air pressure compared to Roots superchargers.
3. Twin-Screw Supercharger
Similar to Roots superchargers in design but with a pair of intermeshing screws instead of lobes. Often found in high-performance and aftermarket applications.
4. Electric Supercharger
Utilizes an electric motor to drive the compressor, providing on-demand boost without being mechanically linked to the engine.
5. Mechanical Belt-Driven Supercharger
Typically connected to the engine’s crankshaft via a belt, the mechanical supercharger increases air intake. Commonly seen in older, classic cars, and can be driven by a belt connected to the engine.
6. Vane Supercharger
Also known as a centric vane-type supercharger. Utilizes adjustable vanes in the compressor housing to control the airflow and optimize efficiency at different engine speeds.
Which Type Of Supercharger Is Best?
The choice between centrifugal and other types of superchargers depends on specific performance goals and vehicle characteristics.
Centrifugal superchargers are known for efficiency and denser air, making them suitable for certain applications, but roots and twin-screw superchargers also have their advantages in different scenarios.
Drive System of Supercharger
Various techniques are employed to operate a supercharger effectively.
- Direct drive
- Belt (V-belt, flat belt, synchronous belt)
- Gear drive
- Variable speed ratio
- Chain drive
How Does A Supercharger Work?
Here’s a basic overview of how a supercharger works:
1. Air Compression
The supercharger is typically driven by the engine’s crankshaft via a belt. As the engine rotates, the supercharger spins and draws in air.
2. Air Intake
The supercharger pulls air from the outside environment and compresses it before delivering it to the engine’s intake manifold. This compressed air contains more oxygen molecules than the ambient air.
3. Increased Oxygen
By forcing more air into the combustion chamber, the engine can burn more fuel. The increased oxygen allows for a more efficient and powerful combustion process.
4. Improved Power Output
The enhanced combustion results in increased power and torque, leading to improved engine performance. This is especially beneficial at higher RPMs where an engine might struggle to draw in enough air on its own.
How Does A Supercharger Pull In Air?
A supercharger pulls in air by utilizing a belt-driven compressor connected to the engine’s crankshaft. As the engine rotates, the supercharger’s compressor spins and draws in air.
This compressed air is then forced into the engine’s combustion chambers, allowing for a higher air-to-fuel ratio and increased power output. The process enhances engine performance by providing more oxygen for combustion, resulting in improved efficiency and horsepower.

Supercharger Price
The price of using a supercharger can vary depending on location and charging network. Tesla’s Supercharger network typically charged between $0.25 and $0.50 per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
Supercharged Cars
Here are some examples:
- Dodge Challenger SRT Hellcat
- Chevrolet Camaro ZL1
- Mercedes-Benz SLC-Class
- Land Rover Range Rover
- Mini Hatch
- Audi S5
- Chevrolet Corvette ZR1
- Aston Martin V600
- Jaguar XJR
- Toyota MR2
- Volvo S90
- Ariel Atom
- Shelby GT500
- Audi S4
- Chevrolet Cobalt SS
- Chevrolet Impala SS
- Jaguar XF
- Lotus Elise SC
- Mazda Millenia
- Mercedes SSK
- Mustang Cobra SVT
- Aston Martin DB7
- Buick Riviera
Supercharger Diagram
Read More About 6.7 Powerstroke Oil Pan Upgrade: Boost Engine Performance & Life (2024)
Inside A Supercharger
Let’s break down the components you mentioned:
1. Volute
The volute is the outer casing or housing of the supercharger. It is designed to guide and direct air smoothly through the supercharger.
2. Impeller
The impeller is a key component inside the supercharger.
3. Diffuser
The diffuser is located after the impeller and is part of the compressor housing. Its purpose is to slow down the high-speed, compressed air from the impeller.
4. Transmission
The transmission in a supercharger is responsible for transferring power from the engine to drive the impeller.
Supercharger Brands
Here are some well-known supercharger brands:
- Eaton
- IHI Machinery and Furnace Co. Ltd.
- Kenne Bell
- HARROP USA
- Duryea Technologies
- ProCharger
- Magnuson Products LLC
Advantages of Supercharger
Here are some advantages of using a supercharger:
- Increased Power and Performance
- Instant Power Boost
- Consistent Power Delivery
- Improved Torque
- Enhanced Engine Efficiency
- Compact Design
- Cooler Intake Air Temperatures
- Simpler Installation
- No Need for Exhaust Gas Energy
- Enhanced Performance at Altitude
Disadvantages Of Supercharger
While superchargers offer several advantages, they also come with certain disadvantages.
- Complex Installation: Installing a supercharger can be a complex process that requires technical expertise.
- Maintenance Requirements: Superchargers require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: While superchargers increase horsepower, they can negatively impact fuel efficiency.
- Increased Heat Generation: Superchargers generate heat during operation.
- Engine Stress: Superchargers put additional stress on the engine due to increased air and fuel combustion.
- Limited Power Gains at Higher RPMs: May decrease at higher RPMs, limiting the overall power gains.
- Compatibility Challenges: Not all engines are easily adaptable to superchargers.
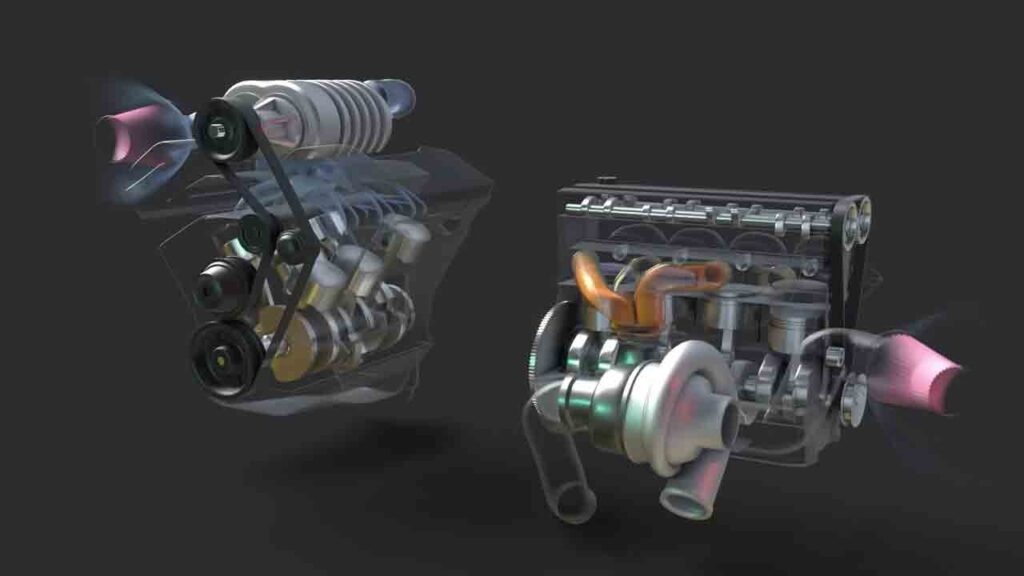
Working Of Turbocharger
A turbocharger consists of a turbine and a compressor mounted on a common shaft. Exhaust gases spin the turbine, which drives the compressor to compress incoming air, increasing its density.
This compressed air is then delivered to the engine, enhancing combustion and boosting overall performance.
What Is A Procharger?
A Procharger is a brand of centrifugal supercharger, a device that compresses air to enhance combustion in an internal combustion engine, resulting in increased horsepower and performance.
How Does A Turbocharger Work?
A turbocharger works by using exhaust gases to drive a turbine, which is connected to a compressor. The compressor forces more air into the engine, allowing for increased fuel combustion and higher power output.
How Much Hp Does A Turbocharger Add?
Generally, it can range from 70 to 150 horsepower, but individual results may differ.
What Is Turbocharging?
Turbocharging is a method of increasing internal combustion engine efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, allowing for enhanced fuel combustion and increased power output.
What Is A Turbocharger?
A turbocharger is a device that increases an internal combustion engine’s efficiency and power by forcing more air into the combustion chamber. It uses exhaust gases to drive a turbine.
Turbo Vs Twin Turbo
Here’s a basic comparison:
| Feature | Turbo | Twin Turbo |
| Number of Turbos | 1 | 2 |
| Response Time | Slower than Twin | Faster due to smaller turbos |
| Power Delivery | Linear power curve | Smoother and more immediate |
| Efficiency | Typically less efficient than Twin | Can be more efficient at lower RPMs |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Usually more expensive due to complexity |
| Complexity | Simpler design | More complex due to dual turbos |
| Installation Space | Requires less space | Requires more space |
| Top-End Power | May lack top-end power compared to Twin | Can provide better top-end power |
| Maintenance | Generally easier to maintain | Potentially more maintenance due to dual systems |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Fuel Efficiency | May be less fuel-efficient at lower RPMs | Can offer better fuel efficiency at lower RPMs |
Supercharger Vs Turbocharger
| Feature | Supercharger | Turbocharger |
| Power Source | Driven by the engine’s crankshaft via a belt | Driven by exhaust gases |
| Response Time | Immediate (virtually no lag) | Lag may be present due to exhaust gas-driven mechanism |
| Efficiency | Slightly less efficient as it consumes engine power to operate | Generally more efficient as it utilizes waste exhaust energy |
| Installation | Generally easier and quicker to install | Installation can be more complex due to exhaust system modifications |
| Maintenance | Typically requires more frequent maintenance | Generally has lower maintenance requirements |
| Cost | Initial cost may be lower | Initial cost can be higher, but fuel efficiency gains may offset |
| Fuel Efficiency | May have a slightly greater impact on fuel consumption | Can contribute to better fuel efficiency, especially at cruising speeds |
| Application Range | Well-suited for low-end torque and immediate power delivery | Effective at higher RPMs and can provide a power boost across a wider RPM range |
Read Also Oil Air Separator Vs Catch Can: Comprehensive Guide And Differences In Functionality
Supercharger Vs Turbo Sound
Turbochargers often create a whooshing or whistling sound due to the turbine’s spooling.
Superchargers generate a consistent whine or growl, reflecting the mechanical rotation of their components.
Can A Car Have Both Turbo And Supercharger?
Yes, a car can have both a turbocharger and a supercharger. This combination is known as twin-charging. The supercharger provides immediate power at lower RPMs, while the turbocharger kicks in at higher RPMs, providing additional boost.
FAQs
How does a supercharger work simple?
A supercharger forces more air into the engine, enhancing combustion, and increasing power output by compressing air before entering cylinders.
Is A supercharger better than a turbo?
The preference between a supercharger and a turbocharger depends on specific needs. While turbos can enhance fuel economy and reduce emissions, superchargers provide more immediate power, offering advantages in certain applications.
How does a supercharger get air?
A supercharger forces more air into an engine by using a belt-driven compressor, increasing combustion efficiency and boosting performance.
Is a supercharger AC or DC?
A supercharger typically uses a DC (direct current) motor to compress air and increase the intake of air into an internal combustion engine.
Why are superchargers so fast?
Superchargers are fast because they deliver electricity directly to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger, ensuring a quicker charging process.
What is the most common type of supercharger?
The Roots-type supercharger is the most common type.
Do superchargers need intercoolers?
Yes, intercoolers are necessary for superchargers to cool the compressed air and improve engine performance by increasing air density.
Do superchargers have compressors?
Yes, superchargers have compressors.
Who invented the supercharger?
The supercharger was invented by Gottlieb Daimler.
Do superchargers have a clutch?
No, superchargers generally don’t have clutches. They are mechanically driven by the engine via a belt or gear system.

Conclusion
Understanding how does a supercharger work unveils the mechanical prowess behind enhancing internal combustion engines. With various types like Roots, Centrifugal, and Twin-Screw, each serves specific performance goals. The choice between supercharger and turbocharger depends on individual needs, offering unique advantages.
Whether enjoying the immediate power of a supercharger or the efficiency of a turbocharger, both contribute to elevating engine performance in different ways.




